最高のコレクション average yield stress formula 589391-How to calculate yield stress formula
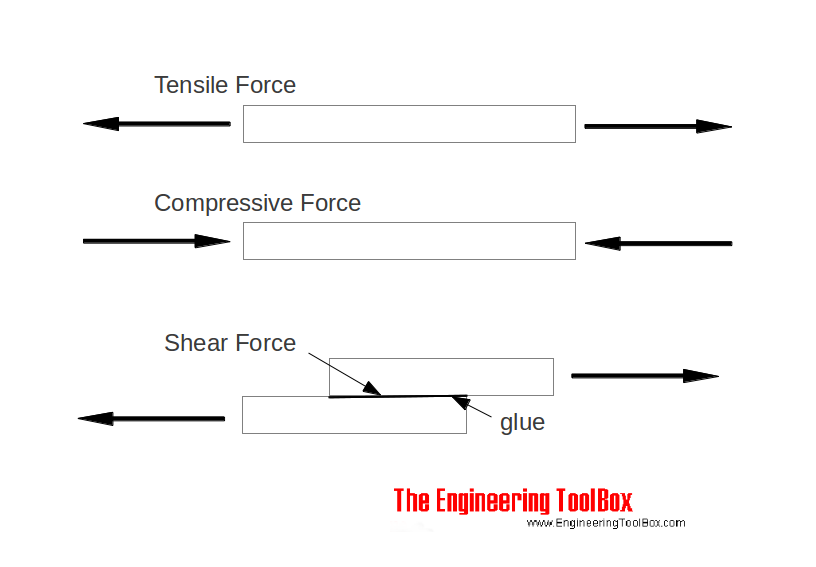
Tensile or compressive stress normal to the plane is usually denoted "normal stress" or "direct stress" and can be expressed as σ = F n / A (1) where σ = normal stress (Pa (N/m 2), psi (lb f /in 2)) F n = normal force acting perpendicular to the area (N, lb f) A = area (m 2, in 2)A video of a tensile test of steel is available here https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=sQkI_Nj1AxsA video demonstrating how to calculate proof stress is availTensile Yield Strength Unit Conversion Calculator;
Solved A Leaf Spring In An Automobile Is Subjected To Cyclic Stresses Course Hero
How to calculate yield stress formula
How to calculate yield stress formula-The working stress or allowable stress is the maximum safe stress a material may carry The working stress should not exceed proportional limit Since the proportional limit is difficult to determine accurately, we take yield point or the ultimate strength and divide this stress by a suitable number N, called the factor of safetyPer Shigley, the proof strength is approximately equal to 85% of the tensile yield strength, S tyBased on S proof = 085·S ty, the recommended preload force as a function of yield strength is Considering that the above values are conservative, a general rule of thumb is to preload the fastener to 2/3 of the yield strength (ie % yld = 667%)


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I
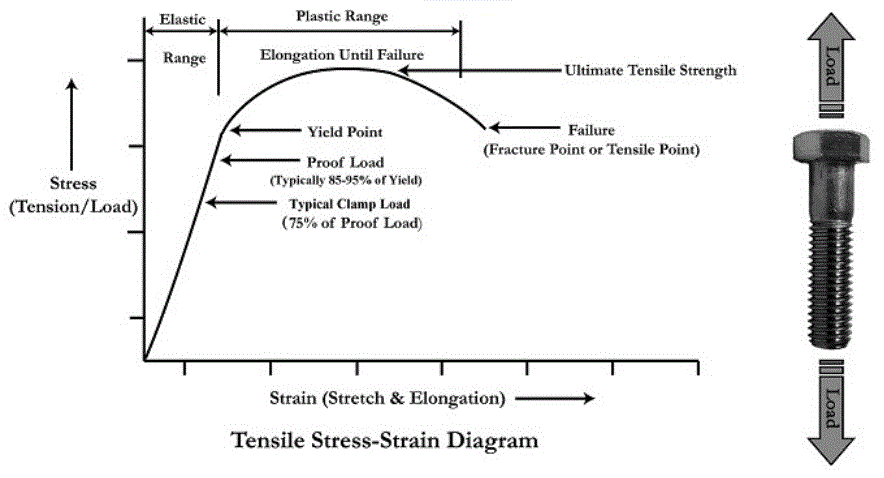
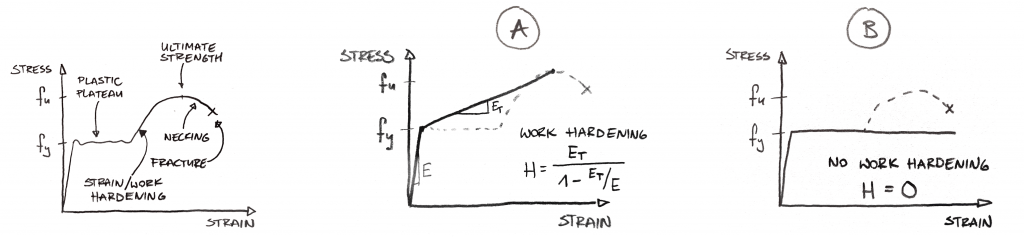
Stress (perform like a plastic) B= Yield strength (point B in fig b) – Stress that will induce permanent set (an offset to the original length) – In fig b, line OC = the offset, line BC is parallel to OA Ultimate strength (see in fig a) – The maximum engineering stress before rupture – Different from the true stress due to 'necking'The yieldtoweight ratio is the amount of weapon yield compared to the mass of the weapon The practical maximum yieldtoweight ratio for fusion weapons (thermonuclear weapons) has been estimated to six megatons of TNT per metric ton of bomb mass (25 TJ/kg)Yields of 52 megatons/ton and higher have been reported for large weapons constructed for singlewarhead use in the early 1960sThe most common engineering approximation for yield stress is the 02 percent offset rule To apply this rule, assume that yield strain is 02 percent, and multiply by Young's Modulus for your material \sigma = 0002\times E σ = 0002×E
P = (2 St/D) × E × F P = Internal design pressure in psi (kPa) gage S = Yield strength in pounds per square inch (kPa) determined in accordance with paragraph (b) of this section t = Nominal wall thickness of the pipe in inches (millimeters)The working stress or allowable stress is the maximum safe stress a material may carry The working stress should not exceed proportional limit Since the proportional limit is difficult to determine accurately, we take yield point or the ultimate strength and divide this stress by a suitable number N, called the factor of safetySteel stress This is usually taken to be 75% of the steel yield stress to prevent any plastic deformation, although studies have shown that many CRCP pavements have performed adequately even though their steel stress was calculated to be above yield stress (Majidzadeh, 1978 as referenced in AASHTO, 1993 1 )
As yield strength is related to deformation which is a result of applied stress, the SI unit of yield strength is Nm 2 In CGS system, the yield strength is gcm 2 State if the given statement is true or false In drawing deep operations of sheet steels, problems are created by yield point phenomenonThe ultimate strength design method is similar to LRFD There is a nominal strength that is reduced by a factor which must exceed the factored design stress For beams, the concrete only works in compression over a rectangular "stress" block above the na from elastic calculation, and the steel is exposed and reaches the yield stress, F yThe average yield expresses an investment's present or future state Tip In order to calculate the average yield on investments, you must take the investment's net income for the year and divide



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
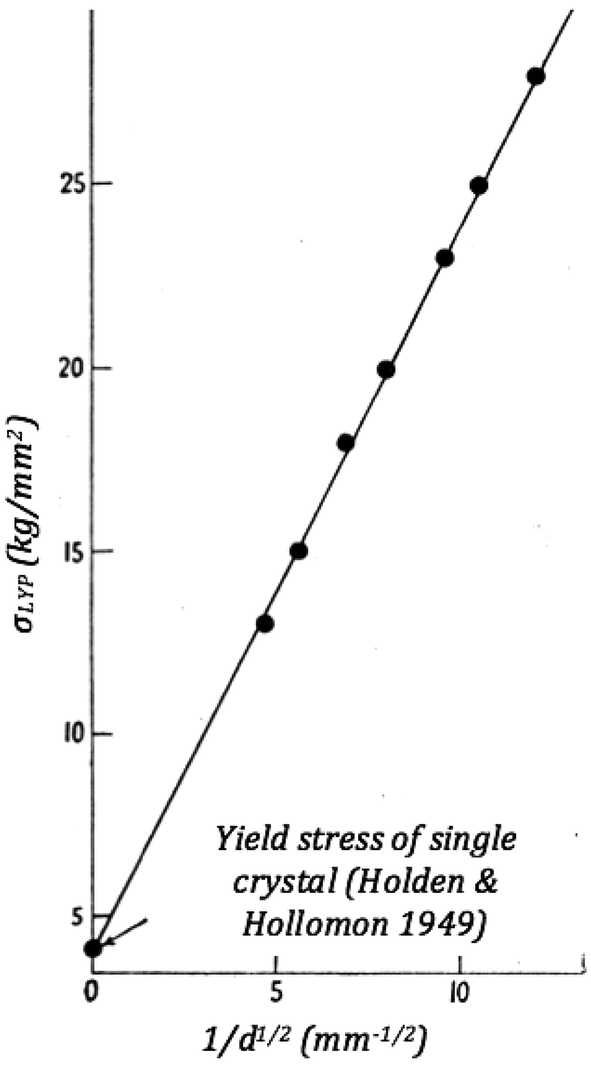
The yield stress is taken to be the peak value of the elastic stress, and the corresponding strain value the yield strain It is important to note that test frequency can influence the measured yield stress based on the relaxation behavior of the material under testStress is the amount of forces (strength or energy) that is being exerted on an object, divided by its crosssectional area to account for size Larger objects are able to withstand higher forcesFor many materials, the yield strength σ varies with grain size according to σ y = σ y,0 k/d x In this expression, termed the Hall–Petch equation , k is a constant, d is the average grain diameter and σ y,0 is the original yield stress


How To Find The Average Bearing Stress Of A Lug Using Abaqus


Solved A Leaf Spring In An Automobile Is Subjected To Cyclic Stresses Course Hero
Yield strength When subjected to stress, a material undergoes recoverable deformation The yield strength of a material represents the stress beyond which its deformation is plastic Any deformation that occurs as a result of stress higher than the yield strength is permanentTwothirds of the specified minimum yield strength (which is at room temperature) Twothirds of the "minimum" yield strength at temperature Average stress for a minimum creep rate of 001%/1000 hours Twothirds of the average stress for creep rupture in 100,000 hours 80% of the minimum stress for a creep rupture in 100,000 hoursBoth formulae cap the column's maximum stress to its yield stress Both the RankineGordon and PerryRobertson formulae are means of determining the maximum average stress ($\sigma = P/A$) a given column can supportDue to the fact that short columns will collapse under compression rather than buckling, it's important that these equations cap the result to the material's compressive yield stress


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau


The Hall Petch And Inverse Hall Petch Relations And The Hardness Of Nanocrystalline Metals Springerlink
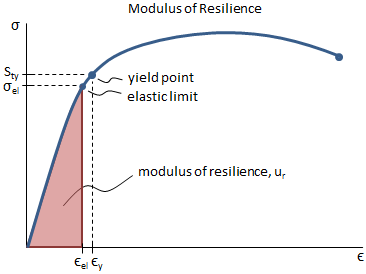
Therefore, an offset yield point is obtained at a strain of 0002 (02%) A straight line is drawn parallel to initial portion of stressstrain curve at the strain value of 0002 and the point where it intersects the stressstrain curve is taken as yield point True StressTrue StrainProblem of wall slippage during yield stress analysis 812 W hen slippage occurs, the measured yield stress is lower than the actual yield stress of the sample and the test results are usually poorly reproducible The dynamic oscillation stress/strain sweep test is an alternative method to analyze the yield behavior of high viscosity materialsWhether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirement



Shear Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Strength At Break Tensile
Use the following calculator to convert yield or tensile values in ksi, Mpa, N/mm² or psi Type the value in the box next to Mpa (using the drop down to change the unit of measurement) ksi MPa N/mm² psi = ksi MPa N/mm² psiThat exhibit distinct yield behavior, the intercept of the line through the stress axis represents a yield stress Comparing the yield stresses for our two sealants we have 170 Pa for sample 1 and 510 Pa for sample 2 It is now a simple matter to set a maximum permissible yield stress for quality control purposesVickers Hardness Calculator Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a material to plastic deformation induced by applied forces Some materials (eg metals, ceramics) are harder than others (eg plastics, wood) Hardness is an important parameter correlating with wear resistance of the mate



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress



Stress Strain Curves Of Metallic Materials And Post Necking Strain Hardening Characterization A Review Tu Fatigue Amp Fracture Of Engineering Materials Amp Structures Wiley Online Library
This would equate to a "yield" of approximately % (90 g divided by 454 g = 198%) This percentage, or the commonly referred to "yield," is a practically meaningless numberThermal Expansion Axial Force Calculator;Yield stress and strength will now be sought Yield Stress Definition Consider a typical, ductile material stress strain curve as shown in Fig 1 Fig 1 Stress strain curve The related constitutive form will be taken to be that of the strain hardening type and applicable to any standard test such as those for



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Strength At Break Tensile
F FORCE SECTION AREA = STRESS= 30 000 N mm X mm STRESS= 30YIELD STRESS MATHEMATIC APPLICATION F/A FORCE AREA = STRESS= FORMULA 1 A sample of steel ( from an engineering company) is given a stress test to assess its yield stress The steel is a mm square section The sample begins to yield at 30 000 Newtons What is the yield stress?Linear expansion due to change in temperature can be expressed as dl = α l o dt (1) where dl = elongation (m, in) α = temperature expansion coefficient (m/mK, in/in o F) l o = initial length (m, in) dt = temperature difference (o C, o F) The strain or deformation for an unrestricted expansion can be expressed as


Q Tbn And9gcrf0yb4daxmcs4hece0wbtm Gkjp Dgiun5uwt1stzt02mpf2vo Usqp Cau



What Is Flow Stress What Is Its Relationship With Yield Stress Quora
Yield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?The magnitude of stress at which this transition occurs is known as the material's yield stress or strength The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior Ductile materials like iron boast higher yield strength values than plastics, such as polyethyleneThis assumes that yield occurs when the shear stress exceeds the shear yield strength τ = σ 1 − σ 3 2 ≤ τ y {\displaystyle \tau ={\frac {\sigma _{1}\sigma _{3}}{2}}\leq \tau _{y}\,\!} Total strain energy theory – This theory assumes that the stored energy associated with elastic deformation at the point of yield is independent of the specific stress tensor


Thread Yield And Tensile Strength Equation And Calculator Engineers Edge Www Engineersedge Com



What Is Flow Stress What Is Its Relationship With Yield Stress Quora
The Casson equation can be written as, where σ 0 is the yield stress and η C is the Casson viscosity, which relates to the high shear rate viscosity The HerschelBulkley model describes nonNewtonian behavior after yielding and is basically a power law model with a yield stress term HerschelBulkley equation is written as follows;Unit Conversion Calculator & Converter for Tensile/Yield & Charpy values Use the following calculator to convert yield or tensile values in ksi, Mpa, N/mm² or psi Type the value in the box next to Mpa (using the drop down to change the unit of measurement)The average yield expresses an investment's present or future state Tip In order to calculate the average yield on investments, you must take the investment's net income for the year and divide



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods
There are instances, for example, where stresses above yield are acceptable You should really refer to the appropriate design standard for the structure, its use, and the classification of the stresses Karl Van Aswegen (Fluid Codes FZ LLE) Safety Factors are not necessarily max stress/yieldThe stress divided by the strain is no longer constant because the material will deform to its original position when the applied stress is removed You can use this yield stress formula to find the yield stress of any material or metal Yield stress equation can be stated as the ratio of yield force to original crosssectional areaYield is different from the rate of return, as the return is the gain already earned, while yield is the prospective return Formula = YIELD(settlement, maturity, rate, pr, redemption, frequency, basis) This function uses the following arguments Settlement (required argument) – This is the settlement date of the security It is a date



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve


Steel Material Properties Steelconstruction Info
Yield stress and strength will now be sought Yield Stress Definition Consider a typical, ductile material stress strain curve as shown in Fig 1 Fig 1 Stress strain curve The related constitutive form will be taken to be that of the strain hardening type and applicable to any standard test such as those forDennis R Moss, Michael Basic, in Pressure Vessel Design Manual (Fourth Edition), 13 Maximum Shear Stress Theory This theory asserts that yielding occurs when the largest difference of shear stress equals the shear yield strengthAccording to this theory, yielding will start at a point when the maximum shear stress at that point reaches onehalf of the uniaxial yield strength, F y* Yield Strength or Yield Stress is a property of the material, and does not vary with geometry It can be safely stated that a steel plate of 5 mm thickness will have the same yield strength as a steel plate of 50 mm thickness So, the answer to


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot



A Normal Stress Strain Curve For Copper Showing The Yield Stress That Download Scientific Diagram
When yield strength is reported, the amount of offset used in the determination should be stated For example, "Yield Strength (at 02% offset) = 51,0 psi" Young's Modulus of Common Engineering MaterialsIf a linear dimension is given as 5" 010", one might say, "the nominal dimension is 5" RE Nominal yield stress trainguy (Structural) 10 Dec 09 47 metman,Shear stress, often denoted by τ (Greek tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section Normal stress, on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Correlation Between Engineering Stress Strain And True Stress Strain Curve
Find the average yield Add the cost yield and the current yield and divide by two for the average yield The answer is 05 plus 04 divided by 2 equals 09 Divide that by 2, which equals 045 or 45 percentThe general formula for bending or normal stress on the section is given by Given a particular beam section, it is obvious to see that the bending stress will be maximized by the distance from the neutral axis (y) Thus, the maximum bending stress will occur either at the TOP or the BOTTOM of the beam section depending on which distance is largerYield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress (usually represented in PSI) that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breaking
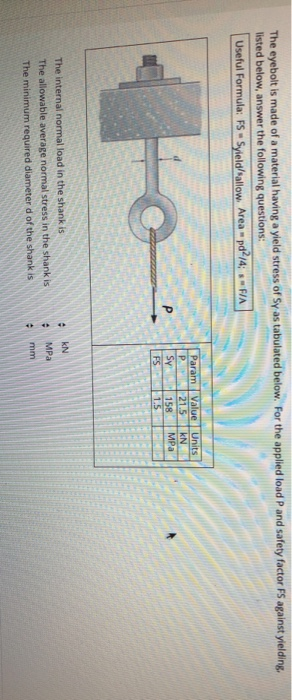


Solved The Eyebolt Is Made Of A Material Having A Yield S Chegg Com
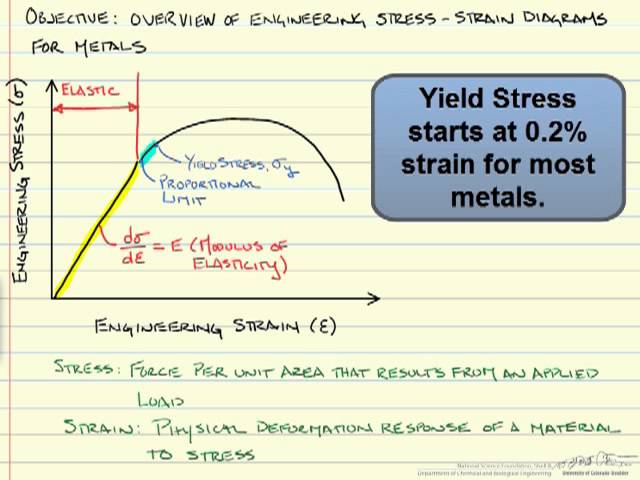


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube
For many materials, the yield strength σ varies with grain size according to σ y = σ y,0 k/d x In this expression, termed the Hall–Petch equation , k is a constant, d is the average grain diameter and σ y,0 is the original yield stressB= Yield point (in fig a) – A stress level beyond which the material would demonstrate high strain for a small stress (perform like a plastic) B= Yield strength (point B in fig b) – Stress that will induce permanent set (an offset to the original length) – In fig b, line OC = the offset, line BC is parallel to OAAs used here (nominal yield stress), I would take it to mean approximately or average yield stress For example;
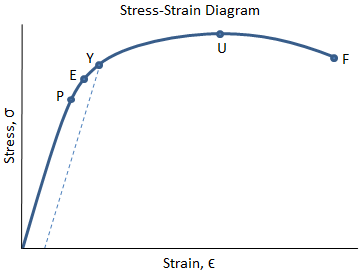


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Equations For Determining The Fatigue Resistance Of Compression Springs
Stress is also related to strain and the young's modulus, which is a ratio of stress to strain in an object under a certain force denoted by this equation E = σ/ε Stress and strain a linearly proportional when the under elastic behavior When an object breaks or starts to yield this relationship no longer holds The following exampleGiven material thickness and bend length as above, the current value I was using for "average yield strength" resulted in a "bottoming" force of 45,300 x 063 x 10 / 00 = 1427 tons Substitution comes up with 49,560 x 063 x 10 / 00 = 1561 tons Or a difference of 134 tons Again, a variance I can live with



Yield Engineering Wikipedia



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve


Strength Of Materials Mechanics Of Materials Mechanicalc
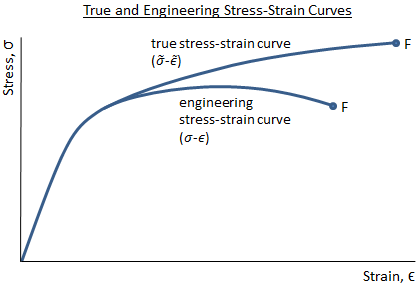


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I


Q Tbn And9gcqajm1wzozitbdfzcet9dxf M3cjyk3ap Wkgrziccwdxqyy Xg Usqp Cau
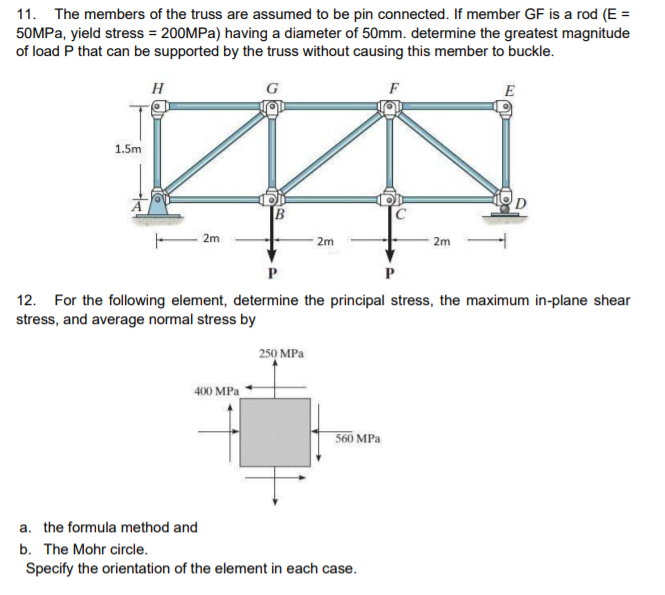


Solved 11 The Members Of The Truss Are Assumed To Be Pin Chegg Com


Engineering Stress Strain Curve
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot



113 Questions With Answers In Yield Strength Science Topic
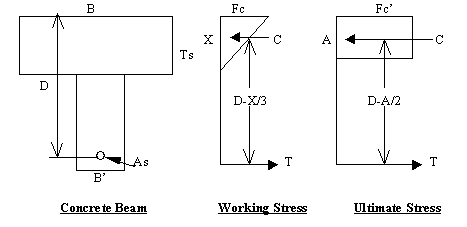


Introduction To Reinforced Concrete Structural Design An Online Course For Engineers And Land Surveyors



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Solved The Yield Strength For An Alloy That Has An Averag Chegg Com



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



True Stress True Strain Models For Structural Steel Elements
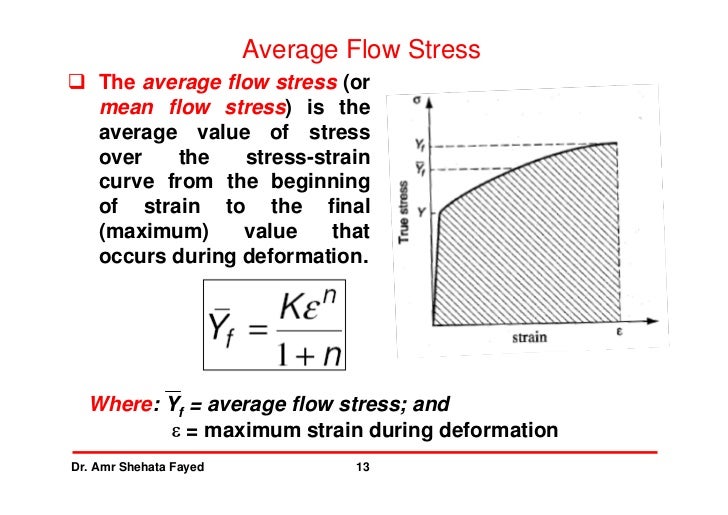


Metal Forming 2
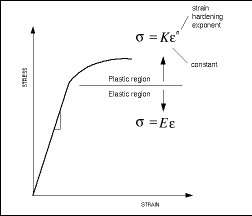


Strain Formula Engineering


Flexural Behavior Of Beams Reinforced With Steel Bars Exceeding The Nominal Yield Strength



Solved The Average Grain Diameter Of A Given Mild Steel I Chegg Com



What S The Difference Between Bearing Shear And Tear Out Stress Machine Design
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods



Calculate Yield Stress Youtube


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau
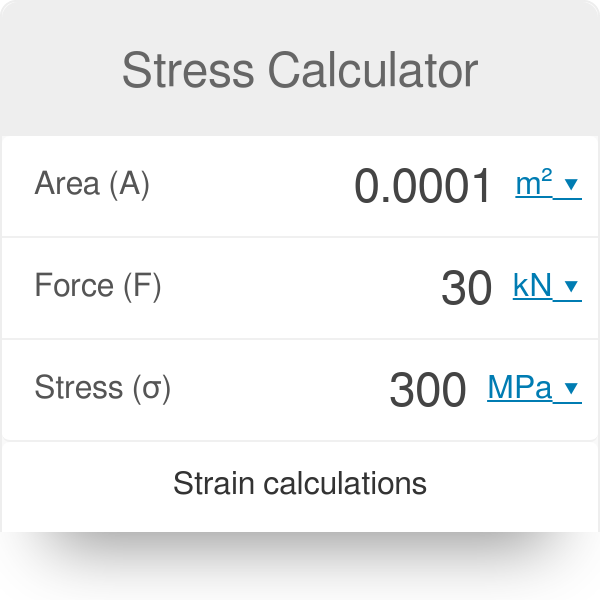


Stress Calculator



Yield Stress An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Cantilever Beam Worked Example



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Mechanics Ebook Normal Strain
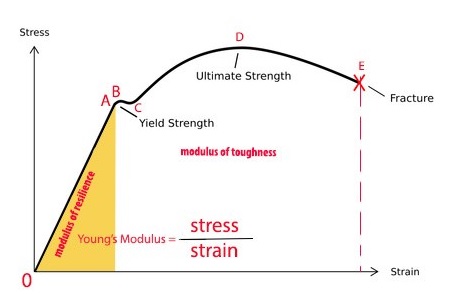


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve
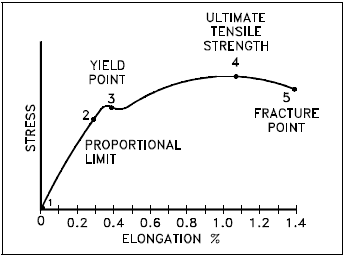


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
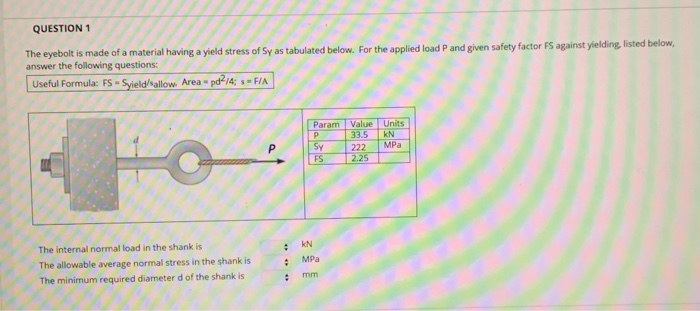


Solved Question 1 The Eyebolt Is Made Of A Material Havin Chegg Com



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Engarc L Offset Yield Method



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


3 1 Axial Strain


What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora


How To Interpret Fea Results Enterfea


Stress Strain And Young S Modulus



Strength At Break Tensile


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Stress Strain Curves Of Metallic Materials And Post Necking Strain Hardening Characterization A Review Tu Fatigue Amp Fracture Of Engineering Materials Amp Structures Wiley Online Library


Www Mdpi Com 75 4701 8 1 11 Pdf



Solved Instructions Utilize The Formulas From Your Equat Chegg Com
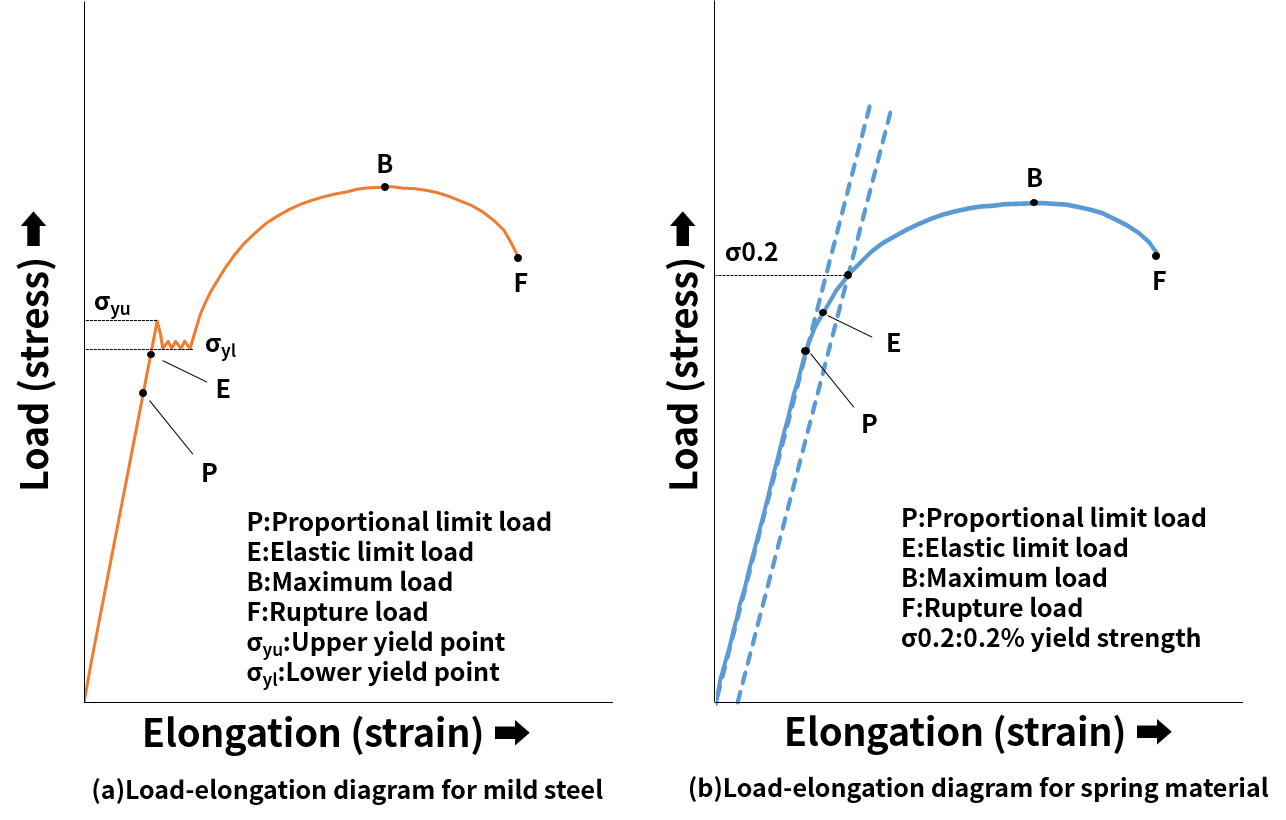


Compression Springs How To Calculate Spring Stress Tokai Spring Industries Inc
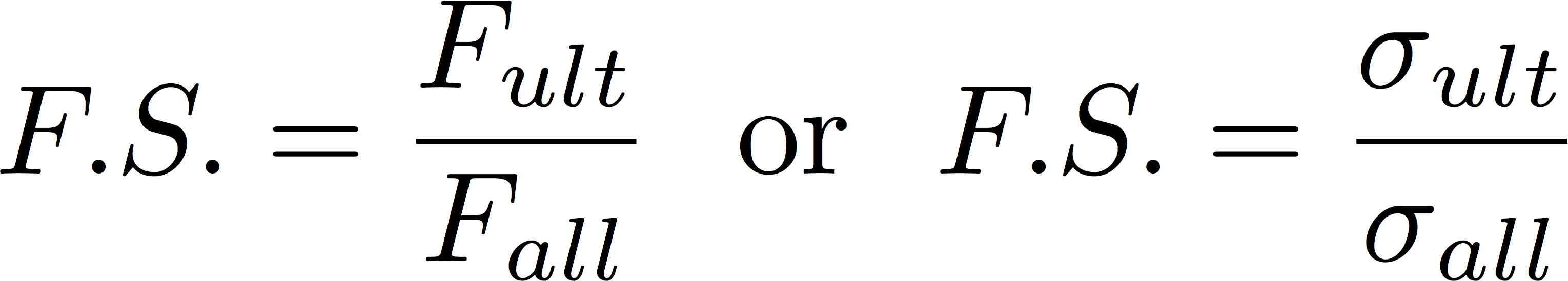


Mechanics Of Materials Stress Mechanics Of Slender Structures Boston University



Solved Instructions Utilize The Formulas From Your Equat Chegg Com



Initial Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Fibre Stress An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Solved Instructions Utilize The Formulas From Your Equat Chegg Com



Draw Stress An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Ocw Tudelft Nl Wp Content Uploads Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter6 Pdf
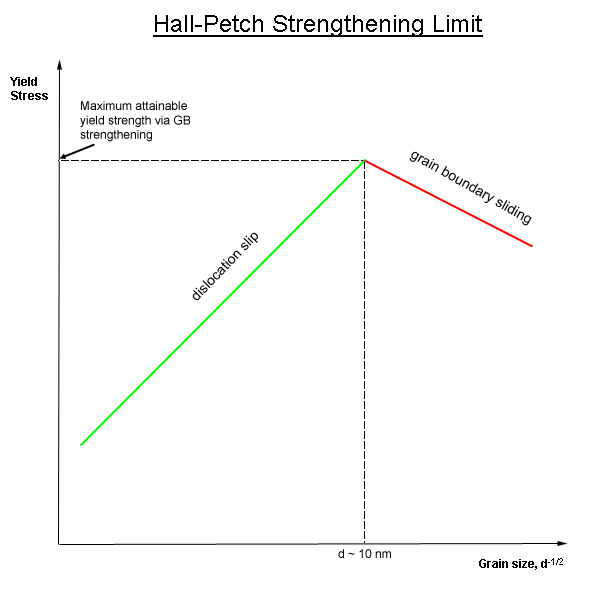


Grain Boundary Strengthening Wikipedia
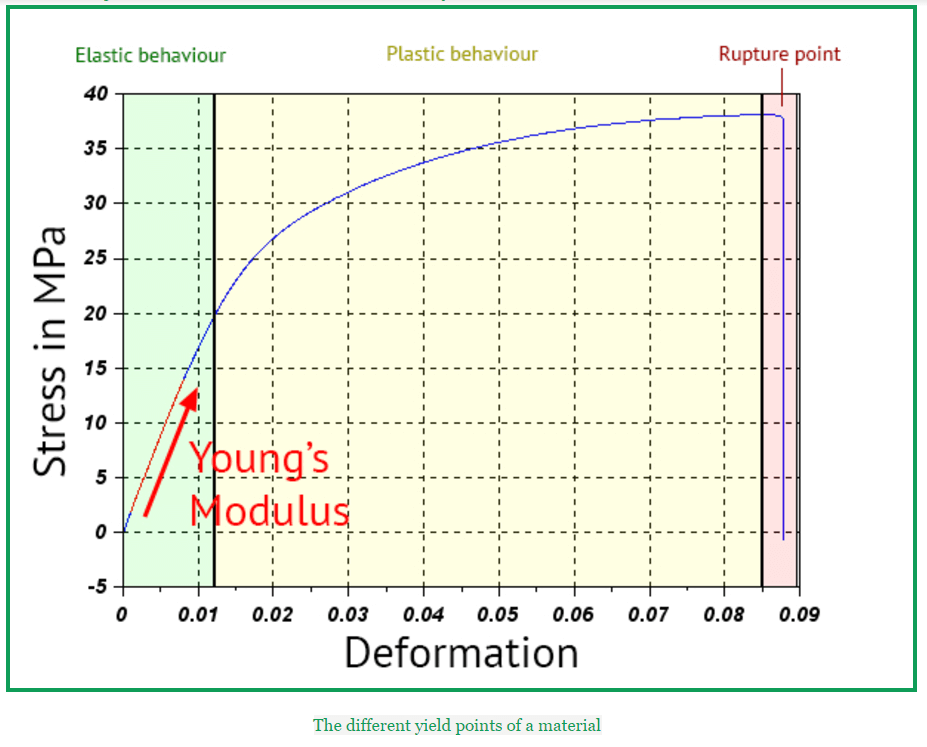


Young S Modulus And Tensile Strength All You Need To Know
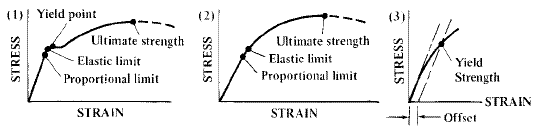


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
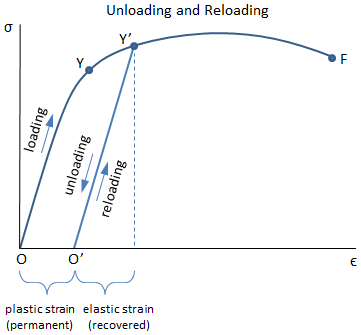


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Normal Stress Differences And Yield Stresses In Attractive Particle Networks



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Virtual Labs


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I
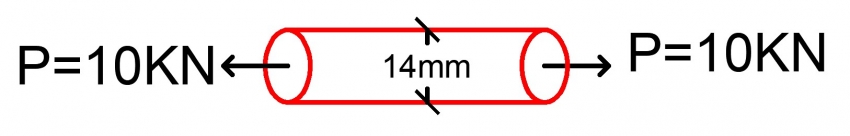


Calculate The Maximum Shear Stress Thestructuralengineer Info



Solved Problem 3 The Yield Strength For An Alloy That Ha Chegg Com



What Is The Difference Betweem True Stress And Flow Stress
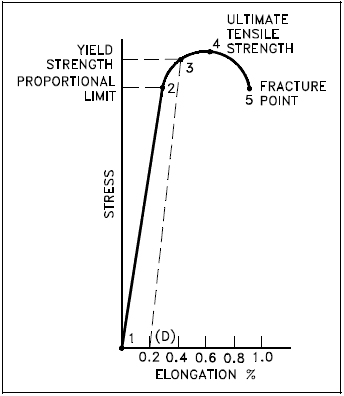


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library
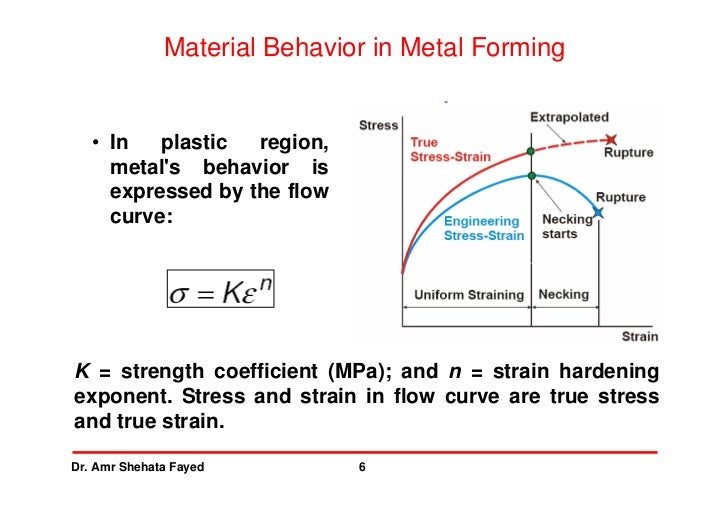


Metal Forming 2
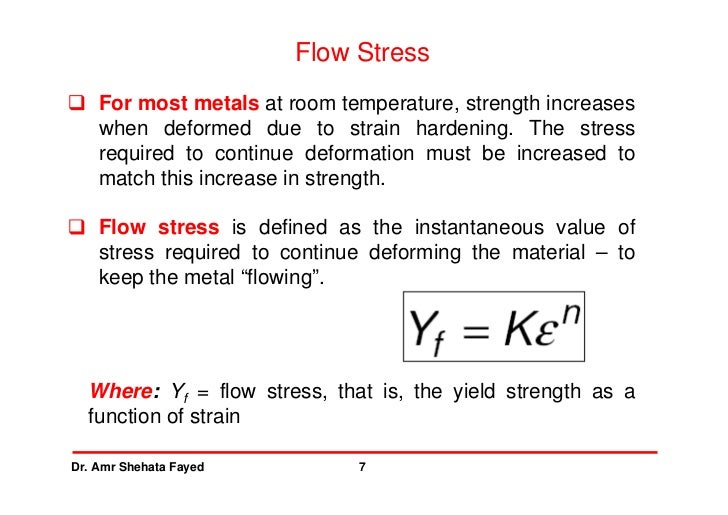


Metal Forming 2



How Can I Determine The 0 2 Yield Stress From My Stress Strain Graphs



Characteristic Strength Of Materials Characteristic Load Or Ultimate Load



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



Flow Curve And Yield Point Determination With Rotational Viscometry Anton Paar Wiki



Critical Resolved Shear Stress Wikipedia
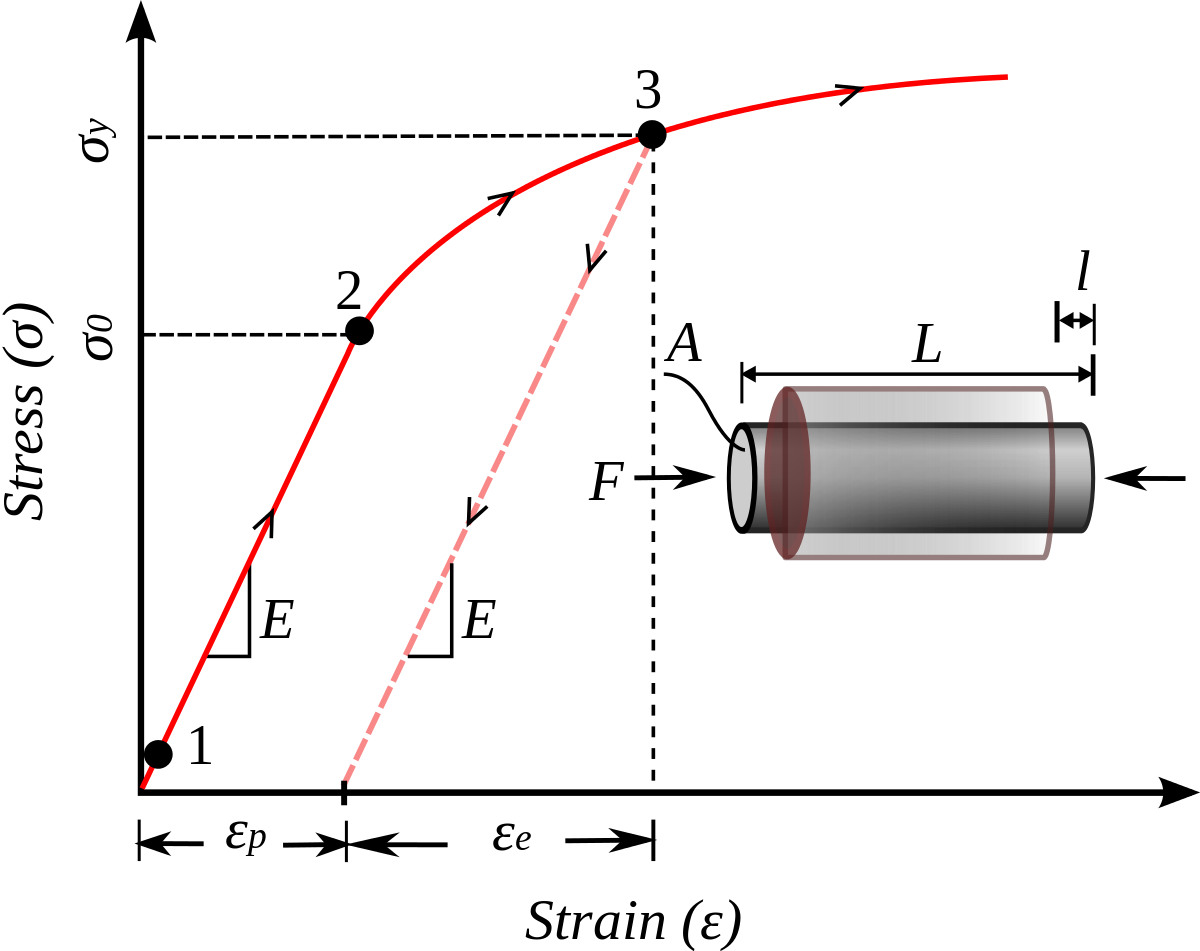


Work Hardening Wikipedia


コメント
コメントを投稿